Vertical farming is the process of growing plants in vertically stacked layers, usually indoors, in buildings called "plant factories". It is a form of urban agriculture that grows crops without the need for natural sunlight, and which has be en practiced for centuries on small scales, but modern technology has enabled this process to be scaled up to grow food for cities.
Vertical farms are a new way to produce food for our ever-growing population.
The world is starving for space. The population is increasing, while we are running out of resources. One solution is to use less land and grow our food on vertical farms. Vertical farms save space and don't require soil or pesticides, they use 95% less water than traditional farms, produce zero emissions, and work 24/7 without the need for humans to monitor them. There are many kinds of vertical farms, from rooftop gardens to warehouse farms and everything in between. Large-scale vertical farms are typically called urban or indoor farming while smaller ones are usually named greenhouses or container gardening.
The main techniques used to grow vertical farms are Hydroponic (Aero) and Aquaponics.
Aeroponics is a method of growing plants with little or no soil by constantly spraying them with a nutrient-rich mist. It’s more efficient in that it uses neither soil nor sunlight, and requires less space.
Aquaponics is a system that combines hydroponics with recirculating aquaculture. It has the benefits of hydroponics and aquaculture, with the added benefits of sterile growing conditions and the elimination of the need for outside inputs such as fertilizer.
Vertical farming global market trends
While the world population levels are continuing to grow, vertical farming has been proposed as a solution to our food shortage problems. Vertical farms could provide enough food to feed an estimated population of 9 billion people by 2050, while using up less than a quarter of the land mass required by traditional agricultural practices.
With over 7 billion people on the planet and counting, the demand for food is at an all-time high. However, it's hard to grow food with conventional methods due to outdated farming techniques, increased land issues, and climate change. Vertical farming solves these problems by significantly reducing the amount of space needed for food production. It's estimated that vertical farms can produce the same number of crops as one acre of land.
The global vertical farming market has been steadily growing over the last years as population size increases and living in urban cities becomes more popular. In 2020, the vertical farming market reached some 5.5 billion U.S. dollars, but the market value is expected to increase to about 20 billion U.S. dollars by 2026. Being able to use vertical space and reducing the need for additional land and construction activity contributes to the appeal of vertical farming in large cities. Demand for vertical farming is expected to increase, largely due to the popularity of organic food.
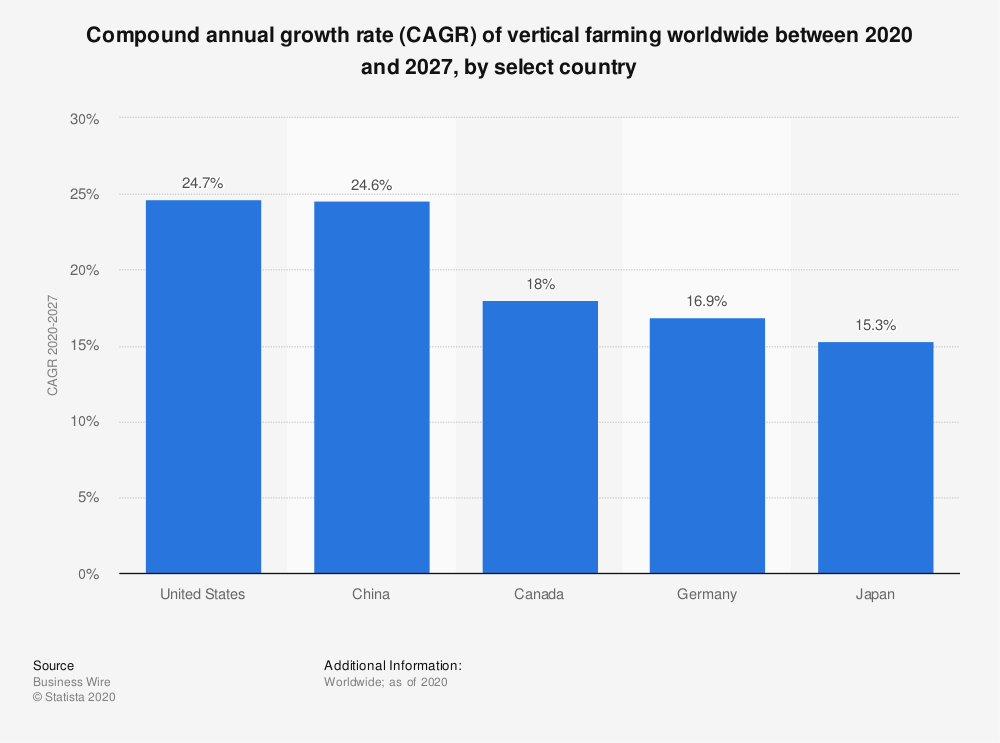
The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of the market for vertical farming in the United States was estimated to be 24.7% between 2020 and 2027. During that time, Canada, Germany, and Japan are respectively expected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 16.9%.New Paragraph